 in the Physical Channel node and select PUSCH to open the Configure PUSCH
window. The following figure shows the Configure PUSCH window with the
default settings.
in the Physical Channel node and select PUSCH to open the Configure PUSCH
window. The following figure shows the Configure PUSCH window with the
default settings.Before adding a PUSCH channel as described below, delete any existing transport channel, physical channel, or resource block collection that occupies the resource blocks that your new PUSCH channel will occupy. If you add a new PUSCH channel without first deleting a conflicting channel or resource block collection, a "code conflicted" error occurs when you generate the waveform.
Click the Add Channel button
 in the Physical Channel node and select PUSCH to open the Configure PUSCH
window. The following figure shows the Configure PUSCH window with the
default settings.
in the Physical Channel node and select PUSCH to open the Configure PUSCH
window. The following figure shows the Configure PUSCH window with the
default settings.
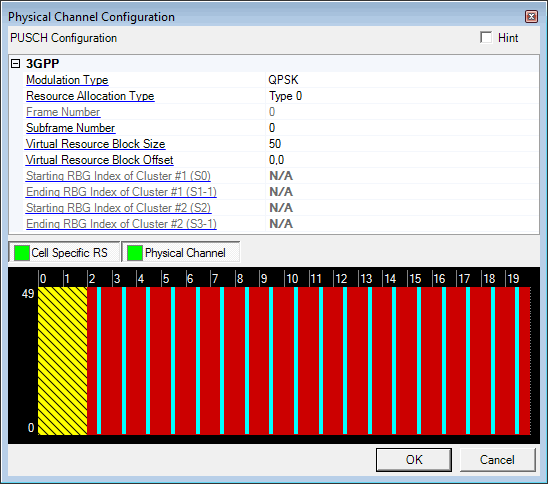
Select QPSK, 16 QAM, or 64 QAM as the modulation type for the PUSCH.
Range: Type 0 | Type 1
Default: Type 0
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the uplink resource allocation type.
Type 0: A set of contiguously allocated virtual resource blocks which are indicated by a starting resource block (Virtual Resource Block Offset) and length (Virtual Resource Block Size).
Type 1: Two sets of resource blocks with each set including one or more consecutive resource block groups of size P (i.e. the same as downlink RBG size for uplink system bandwidth).
For more details, refer to 3GPP TS 36.213.
Only frame 0 is available for the Basic LTE Uplink carrier.
Range: 0 to 9
Default: 0
Enter a subframe number for the PUSCH.
Enter the number of resource blocks the PUSCH will occupy in the frequency domain.
Default: 0,0
Enter a number of resource blocks to offset the PUSCH in each slot, separated by a comma. The first value applies to the even-numbered slot; the second value applies to the odd-numbered slot. The resource block size must be set to a value less than the currently defined system bandwidth in order to set a resource block offset.
Range: 1 to 7 (1.4MHz) | 1 to 9 (3MHz) | 1 to 14 (5MHz) | 1 to 18 (10MHz) | 1 to 20 (15MHz) | 1 to 26 (20MHz)
Default: 1
Enter a value of the Starting RBG Index of Cluster #1 (s0) for each subframe respectively, separated by commas (for example, 0,1,0,1...,0,1).
In the case of Resource Allocation Type = Type 1, this parameter is active. Otherwise the Resource Allocation Type parameter is inactive.
There is an input limitation which is s0 < s1 < s2 < s3. For more details, refer to 3GPP TS 36.213.
Range: 1 to 6 (1.4MHz)
1 to 8 (3MHz) | 1 to 13 (5MHz) | 1 to 17 (10MHz) | 1 to 19 (15MHz) | 1 to 25 (20MHz)
Default: 1
Enter a value of the Ending RBG Index of Cluster #1 (s1-1) for each subframe respectively, separated by commas (for example, 0,1,0,1...,0,1).
In the case of Resource Allocation Type = Type 1, this parameter is active. Otherwise the Resource Allocation Type parameter is inactive.
There is an input limitation which is s0 < s1 < s2 < s3. For more details, refer to 3GPP TS 36.213.
Range: 1 to 7 (1.4MHz) | 1 to 9 (3MHz) | 1 to 14 (5MHz) | 1 to 18 (10MHz) | 1 to 20 (15MHz) | 1 to 26 (20MHz)
Default: 1
Enter a value of the Starting RBG Index of Cluster #2 (s2) for each subframe respectively, separated by commas (for example, 0,1,0,1...,0,1).
In the case of Resource Allocation Type = Type 1, this parameter is active. Otherwise the Resource Allocation Type parameter is inactive.
There is an input limitation which is s0 < s1 < s2 < s3. For more details, refer to 3GPP TS 36.213.
Range: 1 to 6 (1.4MHz) | 1 to 8 (3MHz) | 1 to 13 (5MHz) | 1 to 17 (10MHz) | 1 to 19 (15MHz) | 1 to 25 (20MHz)
Default: 1
Enter a value of the Ending RBG Index of Cluster #1 (s3-1) for each subframe respectively, separated by commas (for example, 0,1,0,1...,0,1).
In the case of Resource Allocation Type = Type 1, this parameter is active. Otherwise the Resource Allocation Type parameter is inactive.
There is an input limitation which is s0 < s1 < s2 < s3. For more details, refer to 3GPP TS 36.213.